| Content | During pregnancy, due to sudden growth in the abdomen or as a result of weight gain or loss, sagging in the abdomen, cracks, etc. There are some undesirable changes. Abdominal stretching helps to reduce these complaints. In fact, the patients with the best results are those who have come because of their sagging after weight loss. Although it is not possible for all the cracks on the abdomen to disappear in tummy tuck surgeries, it is possible to reduce them even more. There is no doubt that it is appropriate to perform this type of surgery by Aesthetic and Plastic surgery specialists, in appropriate operating room conditions and when all conditions that protect the patient are met. |
| GENERAL CARDIOLOGY SCREENING PACKAGE |
| LABORATORY ANALYSIS |
| Glucose |
To determine whether or not your blood glucose level is within normal ranges; to screen for, diagnose, and monitor diabetes, and to monitor for the presence of hypoglycaemia (low blood glucose) and hyperglycaemia (high blood glucose) |
| HbA1c |
To monitor average blood glucose levels over a 3 month period. Used to help diagnose and monitor people with diabetes |
| Urea (Bun) |
To measure how much of waste product you have in your blood. It is used to determine how well your kidneys are working |
| Creatinine |
To assess kidney functions |
| Uric Acid |
To diagnose kidney disorder,diagnose and monitor people with gout, monitor kidney function |
| Complete Urinalysis Test |
To look for metabolic and/or kidney disorders and for urinary tract infections |
| Total Cholesterol |
To screen for risk of developing cardiovascular disease (heart disease, stroke and related diseases); to monitor treatment |
| LDL Cholesterol |
| HDL Cholesterol |
| Triglycerides |
| AST (SGOT) |
To diagnose liver, bile duct and heart diseases |
| ALT (SGPT) |
| Sodium |
To investigate causes of dehydration, oedema, problems with blood pressure, or non-specific symptoms |
| Potassium |
To help diagnose and determine the cause of an electrolyte imbalance; to monitor treatment for illnesses that can cause abnormal potassium levels in the body |
| Calcium |
To scan, diagnose, and monitor a range of conditions relating to the bones, heart, nerves, kidneys, and teeth |
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP) |
To identify the presence of inflammation, to determine its severity, and to monitor response to treatment |
| 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D |
To investigate a problem related to bone metabolism or parathyroid function, possible vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, before commencing specific bone treatment and to monitor some patients taking vitamin D |
| Homocysteine |
To find out if you are at high risk of a heart attack or stroke; also used to determine if you are folate-deficient or vitamin B12-deficient |
| Lipoprotein A |
To evaluate targeted screening for cardiovascular disease (coronary artery disease (CAD) and cerebrovascular disease) risk assessment |
| Blood Count Haemogram |
Haemogram serves as broad screening panel that checks for the presence of any diseases and infections in the body. |
| Troponin |
To see if you have had a heart attack or damage to your heart muscle |
| Vitamin B12 |
To help diagnose the cause of anaemia or neuropathy (nerve damage), to evaluate nutritional status in some
patients, to monitor effectiveness of treatment of B12 or folate deficiency |
| Free T3 |
To help diagnose hyperthyroidism and monitor it's treatment |
| Free T4 |
To diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in adults and to monitor response to treatment |
| TSH |
To screen for and diagnose thyroid disorders; to monitor treatment of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism |
| D- dimer |
To help diagnose or exclude thrombotic (blood clot producing) or bleeding diseases and conditions |
| OTHER ANALYSIS |
| Carotid Ultrasound |
To detect narrowing, or stenosis, of the carotid artery, a condition that substantially increases the risk of stroke |
| Echocardiogram |
To evaluate how your heart moves, heart valves are working and heart’s pumping strength |
| Electrocardiogram |
To measure the electrical activity of the heartbeat and hearth rhythm |
| Exercise Stress Test |
To determine how well your hearth handles work. The test can show if the blood supply is reduced in the arteries that supply the heart |
| EXAMINATIONS |
| Cardiology Examination |
General physical examination, evaluation of the results and recommendations |
| General Surgery Examination |
| Dermatology Examination |
| Today, we cannot talk about that only women prefer face lift operations, which are commonly performed for aesthetic concerns. Face lift procedures, which are also very popular among men of our age, are mostly preferred to recover skin loosening and sagging on the face after a certain age. It is not quite right to talk about an age restriction for facelift procedures, because it is sufficient for the person to feel his own face aged and to detect that the face has lost its dynamics as a result of the examination. | If you are very close to your ideal nose and there is an uncomfortable appearance only at the tip or holes of the nose, a minor surgical intervention is sufficient with today's technology. With tip plasty, it is possible to experience a change in a short time and easily.
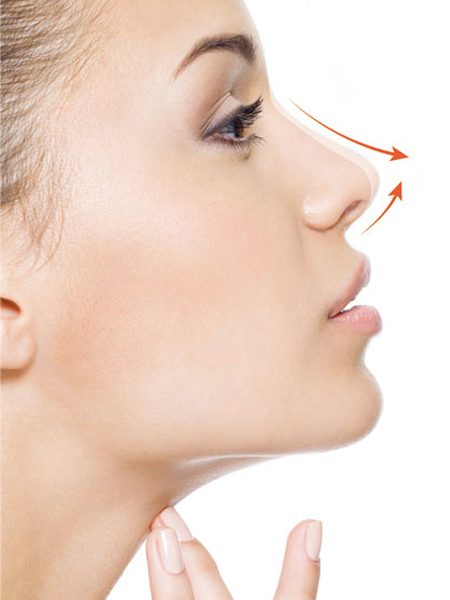
What is Tip plasty?
Tip plasty (nasal tip aesthetics) is the surgery performed to give the desired appearance of the cartilage in the front of the nose without touching the nasal bone, in patients who do not have any curvature or deformation in the nasal bone, but have curvature, width, coarseness, irregularity in the nasal anterior cartilage, or wideness in the nostrils.
How long does nose tip plastic surgery take?
The operation takes an average of 20-30 minutes.
Is rhinoplasty a painful operation?
With the drugs given to the nose during the operation, postoperative pain is not felt.
To whom can it be done?
Tip plasty can be performed to beautify the tip of the nose and to eliminate the existing problem in patients who do not have any problems on the back of the nose, the bone structures on the sides of the nose, the septum area in the middle of the nose, the nasal ridge is smooth, the nose is not flattened and wide, and only on the tip of the nose.
With this surgery:
- Thinning the tip of the nose
- Lifting the tip of the nose
- Changing the angle of the nose tip
- Bringing the tip of the nose forward
- Elimination of deformities in the nostrils
- Removal of excess nose wings
- Correction of nasal tip problems can be performed in patients who have had previous nose surgery.
Points to be considered after nasal tip aesthetics and the healing process
Nasal tip aesthetics is a slightly easier surgery with a shorter recovery period compared to other nose surgeries. The patient can return to his daily life in a very short time.
It is recommended to use nasal spray to clean and moisturize the nose after tip plasty. With the cold compress to be applied, the swelling starts to decrease rapidly within 2 days. After the 7th day, the person can easily continue his normal life. The numbness at the tip of the nose may continue for 1 or 2 months. Rapid recovery is achieved in the first 3 months, and full recovery is achieved within 6 to 12 months. | Yaşam Hospital provides the Covid-19 tests in Antalya. With online booking you may have secure and fast results. |
MEN OVER 40 LARGE SCREENING PACKAGE
|
| LABORATORY ANALYSIS
|
| Glucose |
To determine whether or not your blood glucose level is within normal ranges; to screen for, diagnose, and monitor diabetes, and to monitor for the presence of hypoglycaemia (low blood glucose) and hyperglycaemia (high blood glucose) |
| HbA1c |
To monitor average blood glucose levels over a 3 month period. Used to help diagnose and monitor people with diabetes |
| Urea (Bun) |
To measure how much of waste product you have in your blood. It is used to determine how well your kidneys are working |
| Creatinine |
To assess kidney functions |
| Uric Acid |
To diagnose kidney disorder,diagnose and monitor people with gout, monitor kidney function |
| Complete Urinalysis Test |
To look for metabolic and/or kidney disorders and for urinary tract infections |
| Total Cholesterol |
To screen for risk of developing cardiovascular disease (heart disease, stroke and related diseases); to monitor treatment |
| LDL Cholesterol |
| HDL Cholesterol |
| Triglycerides |
| AST (SGOT) |
To diagnose liver, bile duct and heart diseases |
| ALT (SGPT) |
| GGT |
To screen for liver disease or alcohol abuse; and to help your doctor tell whether a raised concentration of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in the bloodstream is due to liver or bone disease |
| ALP |
To screen for or monitor treatment for liver or bone disorder |
| Sodium |
To investigate causes of dehydration, oedema, problems with blood pressure, or non-specific symptoms |
| Potassium |
To help diagnose and determine the cause of an electrolyte imbalance; to monitor treatment for illnesses that can cause abnormal potassium levels in the body |
| Chloride |
To determine if there is a problem with your body’s acid-alkali (pH) balance and to monitor treatment |
| Calcium |
To scan, diagnose, and monitor a range of conditions relating to the bones, heart, nerves, kidneys, and teeth |
| Phosphate |
To help in the diagnosis of conditions known to cause abnormally high or low levels |
| Amylase |
To diagnose pancreatitis or other pancreatic diseases |
| Lipase |
To diagnose and monitor pancreatitis or other pancreatic disease |
| Magnesium |
To measure the concentration of magnesium in your blood and to help determine the cause of abnormal calcium and/or potassium levels |
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP) |
To identify the presence of inflammation, to determine its severity, and to monitor response to treatment |
| 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D |
To investigate a problem related to bone metabolism or parathyroid function, possible vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, before commencing specific bone treatment and to monitor some patients taking vitamin D |
| Blood Count Haemogram |
Haemogram serves as broad screening panel that checks for the presence of any diseases and infections in the body |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
(ESR) |
To detect and monitor the activity of inflammation as an aid in the diagnosis of the underlying cause |
| Ferritine |
To help assess the levels of iron stored in your body |
| Vitamin B12 |
To help diagnose the cause of anaemia or neuropathy (nerve damage), to evaluate nutritional status in some patients, to monitor effectiveness of treatment of B12 or folate deficiency |
| Free T3 |
To help diagnose hyperthyroidism and monitor it's treatment |
| Free T4 |
To diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in adults and to monitor response to treatment |
| TSH |
To screen for and diagnose thyroid disorders; to monitor treatment of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism |
| Beta hCG |
To confirm and monitor pregnancy or to diagnose trophoblastic disease or germ cell tumours |
| HBsAg |
To detect, diagnose and follow the course of an infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or to determine if the vaccine against hepatitis B has produced the desired level of immunity |
| Anti HBs |
| Anti HCV |
To screen for and diagnose hepatitis C virus infection and to monitor treatment of the infection |
| Anti HIV |
To determine if you are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) |
| CEA |
In the presence of certain cancers, CEA may be used to monitor the effect of treatment and recurrence of disease |
| CA 19-9 |
To help tell the difference between cancer of the pancreas and bile ducts and other conditions; to monitor response to pancreatic cancer treatment and to watch for recurrence |
| AFP |
To screen for and monitor therapy for certain cancers of the liver and testes |
| Total PSA |
To help detect and to monitor prostate cancer |
| Free PSA |
| Fecal Direct Parasite Search
(Ova & Parasite Exam) |
To determine whether you have a parasite infecting your digestive tract |
| Fecal Occult Blood Test |
To screen for bleeding from the gut/intestine, which may be an indicator of bowel cancer |
| Abdominal Ultrasound |
To identify diseases at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys |
| Thyroid Ultrasound |
To characterize a thyroid nodule(s), i.e. to measure the dimensions accurately and to identify internal structure and vascularization |
| Carotid Ultrasound |
To detect narrowing, or stenosis, of the carotid artery, a condition that substantially increases the risk of stroke |
| Echocardiogram |
To evaluate how your heart moves, heart valves are working and heart’s pumping strength |
| Electrocardiogram |
To measure the electrical activity of the heartbeat and hearth rhythm |
| Exercise Stress Test |
To determine how well your hearth handles work. The test can show if the blood supply is reduced in the arteries that supply the heart |
| Pulmonary Function Test |
To tests that measure how well your lungs work. |
| Chest X-Ray |
The most commonly preferred diagnostic examination to produce images of heart, lungs, airways, blood vessels and the bones of the spine and chest |
| EXAMINATIONS |
| Internal Medicine Examination |
General physical examination, evaluation of the results and recommendations |
| Cardiology Examination |
| Ophtalmology Examination |
| Pulmonology Examination |
| Urology Examination |
| General Surgery Examination |
| Dermatology Examination |
|
| Additional information |
| Select Hospital |
Antalya Yaşam Hospital, ASV Yaşam Hospital, Alanya Yaşam Hospital, Manavgat Yaşam Hospital
|
|
| Select Hospital |
Antalya Yaşam Hospital, Kemer Yaşam Hospital, ASV Yaşam Hospital, Opera Yaşam Hospital, Alanya Yaşam Hospital, Manavgat Yaşam Hospital
|
| | |
| Select Hospital |
Antalya Yaşam Hospital, Kemer Yaşam Hospital, ASV Yaşam Hospital, Opera Yaşam Hospital, Alanya Yaşam Hospital, Manavgat Yaşam Hospital
|
|
| Select Hospital |
Antalya Yaşam Hospital, Kemer Yaşam Hospital, ASV Yaşam Hospital, Opera Yaşam Hospital, Alanya Yaşam Hospital, Manavgat Yaşam Hospital
|
|






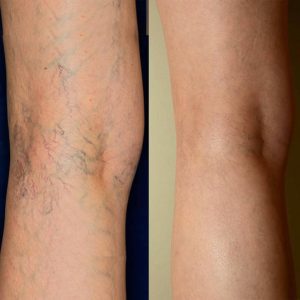
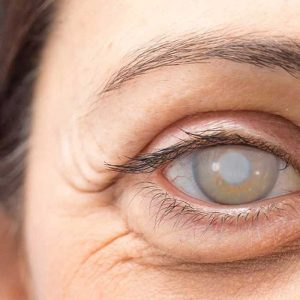
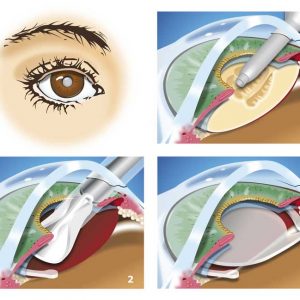

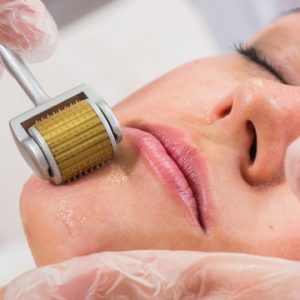









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.