| Content | Jetpeel is a mechanic peeling application by an improved handpeace heading with jet stream towards the skin. It renews, freshens and repairs the skin. Further the skin is slowely peeled and the scratches on the skin resolved with time. Jetpeel also provides attainment of vitamines and repairing substances to the lower layers of the skin. Jetpeel can also trustworthly be applied during summer. 3 sessions with 5 days interval are required. | Today, we cannot talk about that only women prefer face lift operations, which are commonly performed for aesthetic concerns. Face lift procedures, which are also very popular among men of our age, are mostly preferred to recover skin loosening and sagging on the face after a certain age. It is not quite right to talk about an age restriction for facelift procedures, because it is sufficient for the person to feel his own face aged and to detect that the face has lost its dynamics as a result of the examination. |
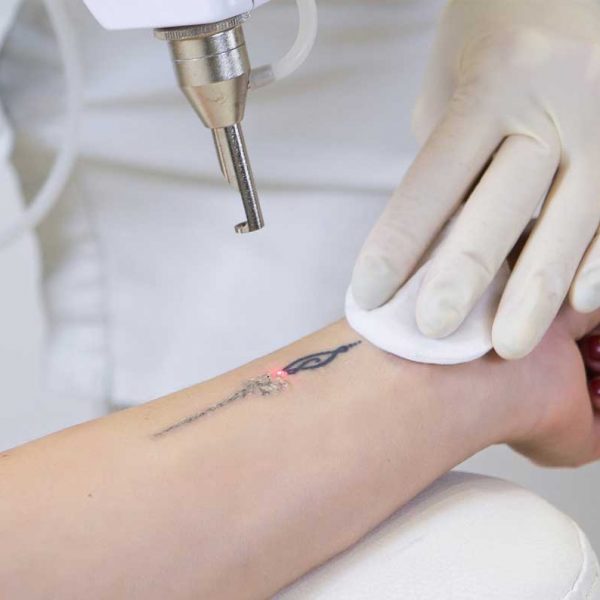
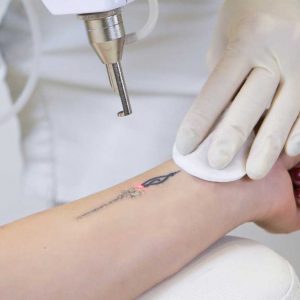
What is laser tattoo removal?
Tattooing is a permanent procedure on the skin. Tattoo removal can be done with modern methods when, for any reason, the person does not want to see his tattoo on his body anymore.
Tattoo removal, permanent make-up and stain treatment can be performed with the Q-switch Nd:YAG laser. This process is a technology that destroys the color pigments used in tattoos by focusing. During this very delicate process, the laser sees and destroys the pigment and damages the tissue as little as possible. In laser tattoo removal, which is a long and laborious process, one hundred percent result may not always be achieved. For this, the decision to have a tattoo should be considered very well, and possible future regrets should be considered.
How is laser tattoo removal done?
Tattoo and skin analysis should be done before the procedure. Lasers designed for tattoo removal and spot treatment send the beam to the epidermis layer of the skin, absorb the compounds that give color to the dermis and subcutaneous tattoo, and destroy the chemical substance by breaking it down. The wavelength of the laser; is adjusted according to the size, density and color of the tattoo.
In laser shots, dye pigments are made without damaging the tissues.
While black dyes under the skin are better detected by the laser, more effective results are obtained, while the same is not true for light-colored dyes.
Different wave sizes are used in tattoos with multi-colored paints.
How many sessions does laser tattoo removal take?
There are some environmental and structural factors in tattoo removal. It is important in which part of the body the tattoo is located. More sessions are required to remove tattoos, especially on the tips of the feet and fingers. For tattoos on larger areas of the body, a more effective process is performed and removed. The duration of the erasing process varies due to the color of the tattoo, the amount and type of paint used in the tattoo. Tattoo removal sessions take place at intervals of approximately 1.5 – 2 months. The number of sessions varies according to the person and the nature of the tattoo.
Will there be any scars after laser tattoo removal?
After each tattoo removal session, the color of the tattoo will lighten by approximately 20%. In tattoos where multi-colored and phosphorescent colors are used, the erasing process may be longer.
Is laser tattoo removal painful?
After numbing the skin part with cream or local anesthesia, the procedure is performed by protecting the upper skin layer in that area with the help of a Q-Switch ND-YAG laser and cooler. After the procedure, there may be bleeding in the area and crusting on the skin that will last for about a few days after the procedure. After the application, antibiotic cream should be used to both repair the area and prevent the development of infection.
When should laser tattoo removal be done?
While tattoo removal is more comfortable in winter, it is not preferred in summer due to the risk of staining with the effect of the sun. The time of the procedure varies according to the size of the tattoo. Since the sun is out in the summer, problems such as permanent staining may occur after the procedure. The best time for this is the winter months. |
| OVERALL CARDIOLOGY SCREENING PACKAGE |
| LABORATORY ANALYSIS
|
| Glucose |
To determine whether or not your blood glucose level is within normal ranges; to screen for, diagnose, and monitor diabetes, and to monitor for the presence of hypoglycaemia (low blood glucose) and hyperglycaemia (high blood glucose) |
| HbA1c |
To monitor average blood glucose levels over a 3 month period. Used to help diagnose and monitor people with diabetes. |
| Urea (Bun) |
To measure how much of waste product you have in your blood. It is used to determine how well your kidneys are working |
| Creatinine |
To assess kidney functions |
| Uric Acid |
To diagnose kidney disorder,diagnose and monitor people with gout, monitor kidney function. |
| Complete Urinalysis Test |
To look for metabolic and/or kidney disorders and for urinary tract infections |
| Total Cholesterol |
To screen for risk of developing cardiovascular disease (heart disease, stroke and related diseases); to monitor treatment |
| LDL Cholesterol |
| HDL Cholesterol |
| Triglycerides |
| AST (SGOT) |
To diagnose liver, bile duct and heart diseases. |
| ALT (SGPT) |
| Sodium |
To investigate causes of dehydration, oedema, problems with blood pressure, or non-specific symptoms |
| Potassium |
To help diagnose and determine the cause of an electrolyte imbalance; to monitor treatment for illnesses that can cause abnormal potassium levels in the body |
| Calcium |
To scan, diagnose, and monitor a range of conditions relating to the bones, heart, nerves, kidneys, and teeth |
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP) |
To identify the presence of inflammation, to determine its severity, and to monitor response to treatment |
| 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D |
To investigate a problem related to bone metabolism or parathyroid function, possible vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, before commencing specific bone treatment and to monitor some patients taking vitamin D |
| Homocysteine |
To find out if you are at high risk of a heart attack or stroke; also used to determine if you are folate-deficient or vitamin B12-deficient |
| Lipoprotein A |
To evaluate targeted screening for cardiovascular disease (coronary artery disease (CAD) and cerebrovascular disease) risk assessment |
| Blood Count Haemogram |
Haemogram serves as broad screening panel that checks for the presence of any diseases and infections in the body. |
| Troponin |
To see if you have had a heart attack or damage to your heart muscle |
| Vitamin B12 |
To help diagnose the cause of anaemia or neuropathy (nerve damage), to evaluate nutritional status in some patients, to monitor effectiveness of treatment of B12 or folate deficiency |
| Free T3 |
To help diagnose hyperthyroidism and monitor it's treatment |
| Free T4 |
To diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in adults and to monitor response to treatment |
| TSH |
To screen for and diagnose thyroid disorders; to monitor treatment of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism |
| D- dimer |
To help diagnose or exclude thrombotic (blood clot producing) or bleeding diseases and conditions |
| OTHER ANALYSIS |
| Carotid Ultrasound |
To detect narrowing, or stenosis, of the carotid artery, a condition that substantially increases the risk of stroke |
| Echocardiogram |
To evaluate how your heart moves, heart valves are working and heart’s pumping strength |
| Electrocardiogram |
To measure the electrical activity of the heartbeat and hearth rhythm |
| Coronary CT Angiography |
It is a imaging method performed by computed tomography of the coronary arteries, which are the vessels that feed the heart, by giving contrast material through the vein of the forearm |
| EXAMINATIONS |
| Cardiology Examination |
General physical examination, evaluation of the results and recommendations |
| General Surgery Examination |
| Dermatology Examination |
| OTHER ANALYSIS |
| Carotid Ultrasound |
To detect narrowing, or stenosis, of the carotid artery, a condition that substantially increases the risk of stroke |
| Echocardiogram |
To evaluate how your heart moves, heart valves are working and heart’s pumping strength |
| Electrocardiogram |
To measure the electrical activity of the heartbeat and hearth rhythm |
| Coronary CT Angiography |
It is a imaging method performed by computed tomography of the coronary arteries, which are the vessels that feed the heart, by giving contrast material through the vein of the forearm |
| EXAMINATIONS |
| Cardiology Examination |
General physical examination, evaluation of the results and recommendations |
| General Surgery Examination |
| Dermatology Examination |
| Aesthetic nose surgery (rhinoplasty) or nose reshaping surgery is the most commonly applied plastic surgery. With aesthetic nose surgery, it is possible to reduce or enlarge your nose, change the shape of the tip or bridge of the nose, narrow the width of your nostrils or change the angle between your nose and upper lip. At the same time, if you have a congenital or injury-related deformity, it can be corrected or some breathing problems can be eliminated. |
| MEN UNDER 40 LARGE SCREENING PACKAGE |
| Glucose |
To determine whether or not your blood glucose level is within normal ranges; to screen for, diagnose, and monitor diabetes, and to monitor for the presence of hypoglycaemia (low blood glucose) and hyperglycaemia (high blood glucose) |
| HbA1c |
To monitor average blood glucose levels over a 3 month period. Used to help diagnose and monitor people with diabetes |
| Urea (Bun) |
To measure how much of waste product you have in your blood. It is used to determine how well your kidneys are working |
| Creatinine |
To assess kidney functions |
| Uric Acid |
To diagnose kidney disorder,diagnose and monitor people with gout, monitor kidney function |
| Complete Urinalysis Test |
To look for metabolic and/or kidney disorders and for urinary tract infections |
| Total Cholesterol |
To screen for risk of developing cardiovascular disease (heart disease, stroke and related diseases); to monitor treatment |
| LDL Cholesterol |
| HDL Cholesterol |
| Triglycerides |
| AST (SGOT) |
To diagnose liver, bile duct and heart diseases |
| ALT (SGPT) |
| GGT |
To screen for liver disease or alcohol abuse; and to help your doctor tell whether a raised concentration of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in the bloodstream is due to liver or bone disease |
| ALP |
To screen for or monitor treatment for liver or bone disorder |
| Sodium |
To investigate causes of dehydration, oedema, problems with blood pressure, or non-specific symptoms |
| Potassium |
To help diagnose and determine the cause of an electrolyte imbalance; to monitor treatment for illnesses that can cause abnormal potassium levels in the body |
| Chloride |
To determine if there is a problem with your body’s acid-alkali (pH) balance and to monitor treatment |
| Calcium |
To scan, diagnose, and monitor a range of conditions relating to the bones, heart, nerves, kidneys, and teeth. |
| Phosphate |
To help in the diagnosis of conditions known to cause abnormally high or low levels |
| Amylase |
To diagnose pancreatitis or other pancreatic diseases |
| Lipase |
To diagnose and monitor pancreatitis or other pancreatic disease |
| Magnesium |
To measure the concentration of magnesium in your blood and to help determine the cause of abnormal calcium and/or potassium levels |
| C-Reactive Protein (CRP) |
To identify the presence of inflammation, to determine its severity, and to monitor response to treatment |
| 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D |
To investigate a problem related to bone metabolism or parathyroid function, possible vitamin D deficiency, malabsorption, before commencing specific bone treatment and to monitor some patients taking vitamin D |
| Blood Count Haemogram |
Haemogram serves as broad screening panel that checks for the presence of any diseases and infections in the body |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
(ESR) |
To detect and monitor the activity of inflammation as an aid in the diagnosis of the underlying cause |
| Ferritine |
To help assess the levels of iron stored in your body |
| Vitamin B12 |
To help diagnose the cause of anaemia or neuropathy (nerve damage), to evaluate nutritional status in some patients, to monitor effectiveness of treatment of B12 or folate deficiency |
| Free T3 |
To help diagnose hyperthyroidism and monitor it's treatment |
| Free T4 |
To diagnose hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism in adults and to monitor response to treatment |
| TSH |
To screen for and diagnose thyroid disorders; to monitor treatment of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism |
| HBsAg |
To detect, diagnose and follow the course of an infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or to determine if the vaccine against hepatitis B has produced the desired level of immunity |
| Anti HBs |
| Anti HCV |
To screen for and diagnose hepatitis C virus infection and to monitor treatment of the infection |
| Anti HIV |
To determine if you are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) |
| Fecal Occult Blood Test |
To screen for bleeding from the gut/intestine, which may be an indicator of bowel cancer |
| OTHER ANALYSIS |
| Abdominal Ultrasound |
To identify diseases at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys |
| Thyroid Ultrasound |
To characterize a thyroid nodule(s), i.e. to measure the dimensions accurately and to identify internal structure and vascularization |
| Echocardiogram |
To evaluate how your heart moves, heart valves are working and heart’s pumping strength |
| Electrocardiogram |
To measure the electrical activity of the heartbeat and hearth rhythm |
| Exercise Stress Test |
To determine how well your hearth handles work. The test can show if the blood supply is reduced in the arteries that supply the heart |
| Pulmonary Function Test |
To tests that measure how well your lungs work. |
| Chest X-Ray |
The most commonly preferred diagnostic examination to produce images of heart, lungs, airways, blood vessels and the bones of the spine and chest |
| EXAMINATIONS |
| Internal Medicine Examination |
General physical examination, evaluation of the results and recommendations |
| Cardiology Examination |
| Ophtalmology Examination |
| Pulmonology Examination |
| Urology Examination |
| General Surgery Examination |
| Dermatology Examination |
|
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.